A string object in ruby holds and manipulates an arbitrary sequence of one or more bytes typically representing characters that represent human language.
Ruby string equality.
Method in the object referred to by variable a is called with b as its argument.
Comparison returns 1 0 1 or nil depending on whether string is less than equal to or greater than other string.
Comparison returns 1 0 1 or nil depending on whether string is less than equal to or greater than other string.
There is a corresponding form of abbreviated assignment operator.
If the strings are of different lengths and the strings are equal when compared up to the shortest length then the longer string is considered greater than the shorter one.
Nil is returned if the two values are incomparable.
Object new object new false string new string.
This works because the string class implements a two equal signs method that knows how to compare strings.
Notice that we use two equal symbols to mean equality.
If the strings are of different lengths and the strings are equal when compared up to the shortest length then the longer string is considered greater than the shorter one.
With an if statement you can check if something is true.
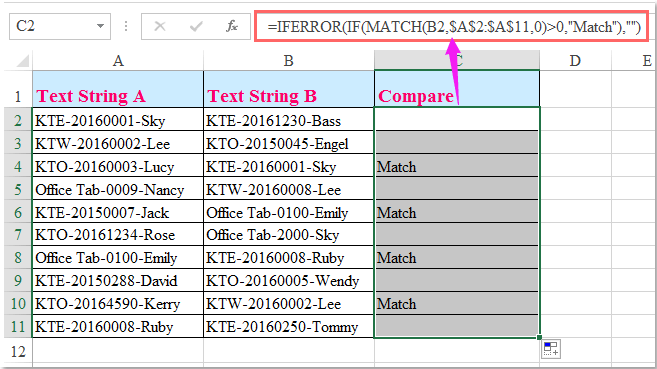
It is not uncommon to need to compare two strings either to assess equality or to find out if one string is higher or lower than the other alphabetically speaking.
Because it s implemented differently in each class it will behave differently depending on the type of object it was called on.
The text within the quote marks is the value of the string this is a simple ruby string literal.
For example a plus.
But when you want to check for the opposite not true false.
Ruby supports a rich set of operators as you d expect from a modern language.
Comparison operators take simple values numbers or strings as arguments and used to check for equality between two values.
B is interpreted as a plus b where the plus.
But what if string didn t implement.
For each operator plus.
Most operators are actually method calls.
Nil is returned if the two values are incomparable.
The simplest string literals are enclosed in single quotes the apostrophe character.
Then ruby would use object s implementation of which defaults to testing for object identity instead of object contents.