Dict text t convenience to create new dynamic instances.
Ruby set variable dynamically.
Well most groans are about how they behave when inheritance enters the fray.
Ruby determines the data type from the data stored in the variable.
So why the bad rap.
To create a variable dynamically one writes a new entry into the global list.
Ruby on the other hand is a dynamically typed language.
Here the two variables can be seen under the single heading f.
You won t see for in very often though.
Template t public struct dynamic var data.
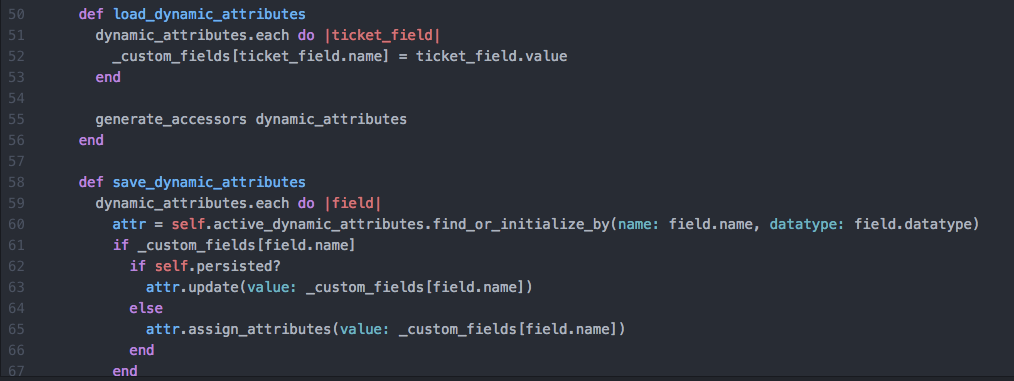
Here s how it works.
This is similar to data types in python and to data types in javascript.
Class variables in ruby have a bad name.
Myusername 10 ruby p enter a variable name x gets.
Ruby arrays are objects and they provide the each method for working with elements.
S myusername myusername s 10.
Firstly it means that you do not need to declare a type when creating a variable.
We can then print the element s value using puts.
A range represents an interval which is a set of values with a start and an end.
And of course all of this is done at runtime.
For each element in the sharks array ruby assigns that element to the local variable shark.
Ranges may be constructed using the s e and s e literals or with range new.
The variable t in the following example can be set to any data type.
To emulate adding a variable to a class instance morfa uses user defined operators and.
Instead the ruby interpreter looks at the type of value you are assigning to the variable and dynamically works out the variable type.
They are special variables that have the appearance of local variables but behave like constants.
Variables in ruby are pass by value not pass by reference some people say that ruby is a pass by reference value language but that s a conversation for another day.
Ruby uses dynamic typing which means type checking is done at runtime rather than compile time as in languages that use static typing.
You cannot assign any value to these variables.
In rlab all the objects are located in a global list.
Consider the following example.
Ruby environment variables ruby interpreter uses the following environment variables to control its behavior.